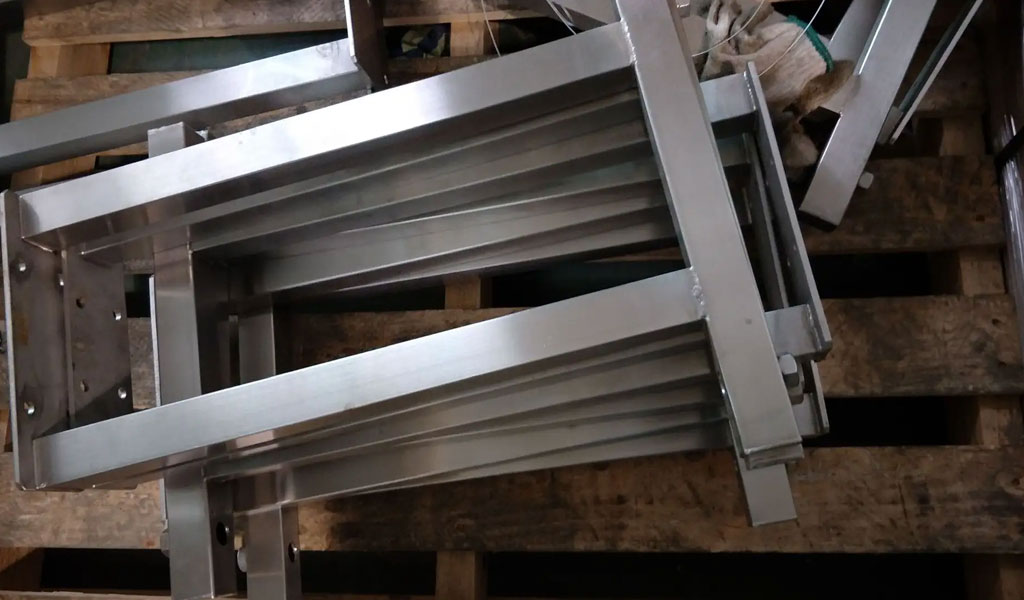
Sheet metal fabrication is the most commonly used metal processing method at present. During the processing of parts, due to the influence of various factors such as the processing accuracy of mechanical equipment, mold wear, and processing errors, the size of the produced sheet metal parts cannot be absolutely accurate. To ensure the availability of workpieces, we must limit the tolerances of sheet metal workpieces to a minimum. So what are the common tolerance standards in sheet metal processing? How should it be marked?Sheet metal fabrication tolerance standard
1. Basic size
Based on the strength and structural requirements of the part, determine the dimensions determined in the design. Preference should be given to standard diameters or lengths.
2. Actual size
Dimensions obtained by measuring.
3. Limit size
Two thresholds for allowing size changes. It is based on the base size. The larger of the two bounds is called the maximum limit size; the smaller is called the minimum limit size.
4. Size deviation (referred to as deviation)
The algebraic difference obtained by subtracting the base dimension of a dimension. Dimensional deviations are as follows:
Upper limit of deviation = maximum limit size – basic size.
Lower limit of deviation = minimum limit size – basic size
The upper and lower deviations can be called limit deviations, and the upper and lower deviations can be positive, negative or zero.
The national standard stipulates that the code name of the upper deviation of the hole is ES, the code name of the lower deviation is EI, the code name of the upper deviation of the shaft is ES, and the code name of the lower deviation of the shaft is EI.
5. Dimensional tolerance (tolerance for short)
The amount of variation in size allowed. Size tolerance = maximum limit size – minimum limit size = upper deviation – lower deviation; since the maximum limit size is always greater than the minimum limit size, that is, the upper deviation is always greater than the lower deviation, the size tolerance must be positive.
6. Standard tolerance and standard tolerance grade
A standard tolerance is any tolerance listed in a national standard for determining the size of a tolerance zone. A standard tolerance class is a class that determines the degree of dimensional accuracy. Standard tolerances are divided into 20 grades, namely IT01, IT0, IT1, IT-18, which represent standard tolerances, and Arabic numerals represent standard tolerance grades, among which IT01 grade is the highest, grades are lowered in turn, and IT18 grade is the lowest. For a certain basic size, the higher the standard tolerance grade, the smaller the standard tolerance value, and the higher the accuracy of the size.
7. Basic deviation
It is used to determine the upper and lower deviations of the tolerance zone relative to the zero line. Generally refers to the deviation close to the zero line
Shaft tolerance codes and standard tolerance class codes consist of two parts and are written with the same number.