Calculating the cost of CNC machining involves a variety of cost factors, including labor, machine, complexity, materials, and more. CNC machining offers one of the most cost-effective options for on-demand production, but customers still require an accurate price estimate before starting a new project. Some machine shops simplify this process with instant online quotes. This article will break down the factors that go into calculating CNC machining costs and provide some tips for optimizing your budget.
CNC Machining And Related Cost Factors
In order to optimize design costs, one should understand the various factors that affect price. Sometimes rethinking materials or surface finishes can significantly reduce the bottom line. Machine shops consider the following key factors when determining project costs:
Precision Machining
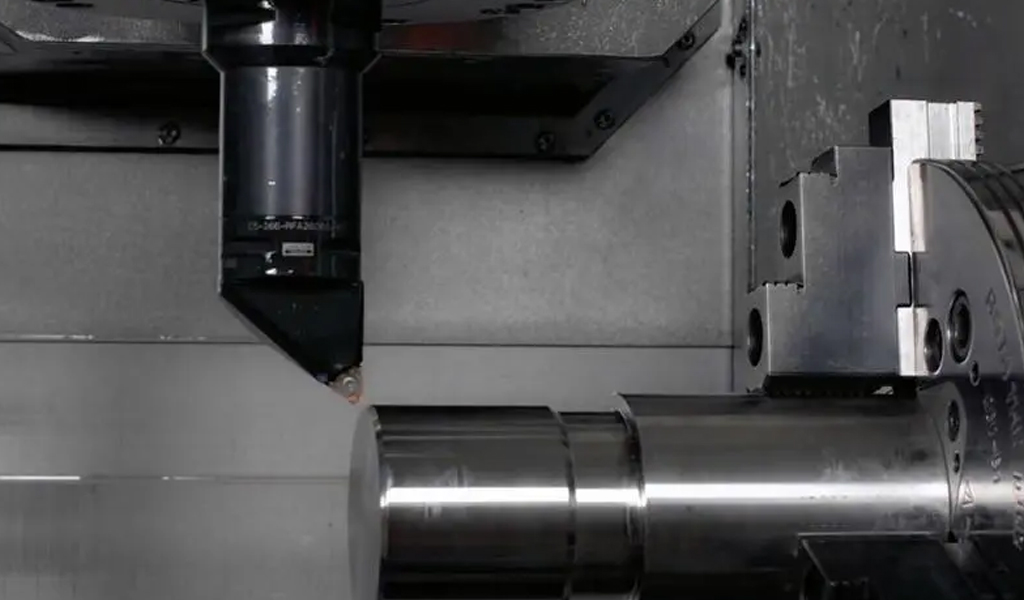
Machine shops use machines such as milling machines and lathes to manufacture parts. 3- and 5-axis mills and lathes provide the flexibility to design parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances. The cost of machining depends on the type of machine and the number of hours it will run, often called machine time. Shops set hourly rates for running different types of machines.
Three-axis milling machines, CNC lathes, 5-axis machines, various machine tools have different charges. These costs have nothing to do with labor. The advantages each machine offers depend on the geometric complexity of the part. The design should be optimized as much as possible before sending it to the machine shop.
Parts Features
Characteristics of a part refer to the geometry and complexity in the design. Parts with complex features require more programming time, run time, and setup time. Complex parts may also require specialized tooling, multiple setups and machines to manufacture, adding to the cost of the final product. It is beneficial to simplify the design as much as possible to reduce the cost of each part. Simplify the design by eliminating unnecessary functionality. In some cases, it may be more cost-effective to break the design into parts and then assemble them.
Material
The cost and workability of the material will be the main factors determining cost.
Subtractive manufacturing processes remove material sequentially, so the amount removed is related to machining time and price. Careful selection of material dimensions can make a significant difference in the calculation of CNC machining costs. If rapid prototyping is required, aluminum and plastic are faster and cheaper to produce. A general rule of thumb is to choose the least expensive material without sacrificing form, fit, or function.
Artificial
CNC machines require little human intervention once set up. A machinist, engineer, or programmer must perform specific steps. These include:
Programming: Programmers convert CAD files into CAM files for CNC machine machining.
Setup: The machinist will set up the machine for production. Someone always needs to cut the blank, place it in the workholding fixture, and then load the tool into the tool changer. The cost depends on the quantity and complexity of the parts produced.
Quality Control: Quality procedures vary from store to store. Typically a store will have a quality team and training, depending on the role.
Post-machining: Part assembly, cleaning, support removal and surface preparation often require manual intervention.
Labor costs for CNC machining are highest at startup, but companies can offset these initial investments in high-volume production.
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment improves the final surface of the part, removing any tool marks or roughness, serving aesthetic purposes and providing wear resistance. The machine shop offers a variety of surface treatments for different materials. Surface preparation affects part tolerances and can range from simple “machining” to more expensive anodizing or sandblasting. Surface finish depends on the part’s application. A qualified machine shop can help determine the most prudent option.
Take an ordinary CNC milling machine machining a part as an example. Assume that the machining material is aluminum alloy, the unit price of the material is 50 yuan/kg, and the dosage is 1kg. The machining technology is simple wire cutting, the machining difficulty is ordinary level, and the machining accuracy requirement is ±0.1mm.
Based on the above information, the following machining cost calculations can be made:
- machining material cost = 50 yuan/kg × 1kg = 50 yuan
- machining cost = 60 yuan/hour × 3 hours = 180 yuan
- Repair cost = 50 yuan/hour × 1 hour = 50 yuan
- Mold manufacturing cost = 100 yuan/hour × 5 hours + 200 yuan = 700 yuan
- Equipment depreciation expense = 10,000 yuan ÷ 5 years × 2 years = 4,000 yuan
- Labor cost = 80 yuan/hour × 3 hours = 240 yuan
- To sum up, the machining cost of this part is: 50 yuan + 180 yuan + 50 yuan + 700 yuan + 4,000 yuan + 240 yuan = 5,220 yuan.